Wedoany.com Report on Feb 7th, The International Energy Agency (IEA) released its Electricity Market Outlook 2026 on the 6th, predicting that global electricity generation will reach several new milestones between 2026 and 2030.

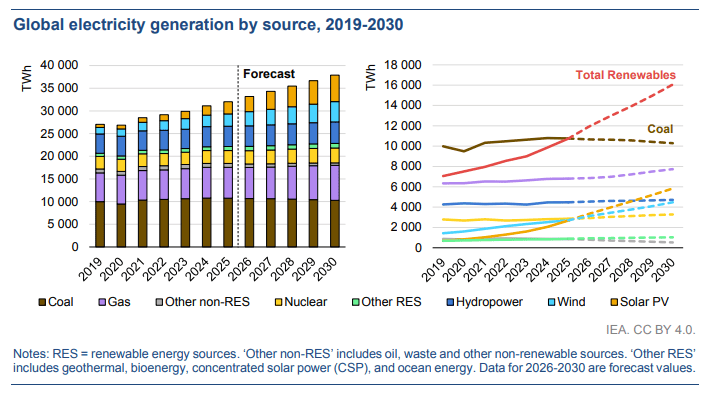
The outlook points out that renewables have already surpassed coal-fired power generation, and nuclear power generation will continue to expand and set new records. Constrained by the growth of low-emission energy sources, global coal-fired power generation is expected to decline slightly. By 2030, new demand will be met by renewables, natural gas, and nuclear power. By 2030, the share of global electricity generated from renewables and nuclear power will reach 50%. The strong growth of renewables and the steady increase in nuclear and gas-fired power generation in many regions will displace global coal-fired power generation over the forecast period. The use of coal in the power sector is expected to shift into a declining trend, with its share in the power mix falling from 34% in 2025 to 27% in 2030.
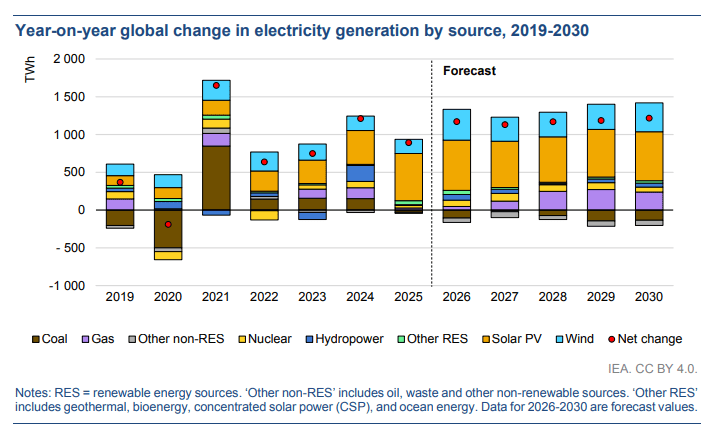
During the forecast period, nuclear power generation is expected to grow by an average of 2.8%, more than double the 1.3% growth rate from 2021-2025. This growth is primarily driven by the commissioning of new reactors in China, India, South Korea, and other countries, restarts in Japan, and strong generation in France due to planned and progressed maintenance. Nuclear power generation in the United States and the European Union is expected to remain relatively stable over the forecast period, while China's nuclear power generation is expected to grow strongly, with nearly 30 gigawatts of new nuclear capacity expected to be added in China during the five-year forecast period of 2026-2030.
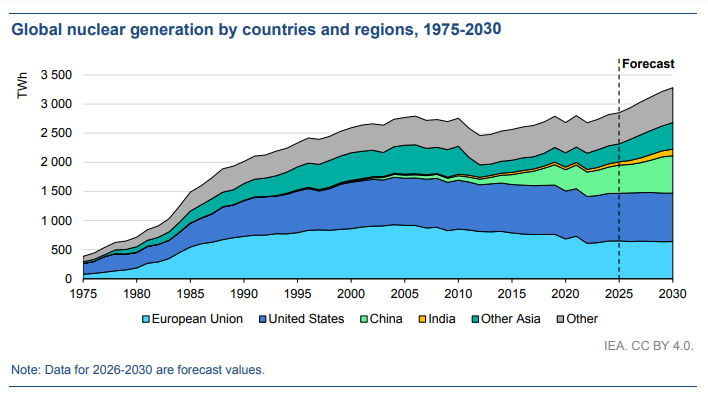
By 2030, China's nuclear power generation is expected to grow by nearly 6% on average annually, while nuclear power generation in the US and EU is expected to remain largely stable. Consequently, China's share of global nuclear power is projected to rise from 17% in 2025 to 20% in 2030, while the US share is expected to fall from 29% to 25%, and the EU share from 23% to 20%. Despite these declining shares, increasing nuclear power generation remains a significant endeavor.
The United States is a key focus, with new small modular reactor (SMR) capacity planned to come online shortly after the end of the 2026-2030 forecast period. Many countries in the European Union also show strong interest and have policies in place to extend the lifetimes of nuclear plants and expand nuclear capacity.
Globally, small modular reactors (SMRs) are receiving significant attention from both the public sector and private enterprises (e.g., large tech companies), as their modular design and smaller scale make them more attractive for private sector financing and deployment. However, as highlighted in the IEA's 2025 report The Path to a New Era for Nuclear Energy, the success of this technology depends on government commitment and supportive policies, timely regulatory design reviews, continued innovation from technology developers, and financing from both public and private sectors.