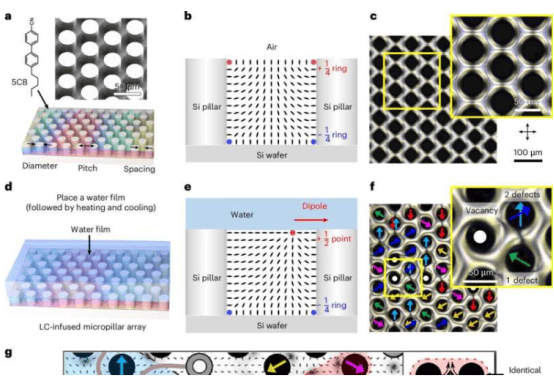
A research team from Nagoya University and Keio University has published groundbreaking results in npj Regenerative Medicine, successfully directly reprogramming mouse embryonic fibroblasts into alveolar type 2 (AT2)-like cells. The technique takes only 7–10 days—two-thirds shorter than conventional stem-cell differentiation methods—offering new hope for treating lung diseases.
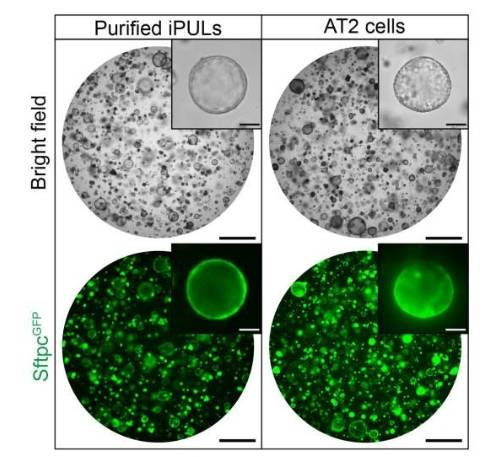
After screening 14 lung-development-related genes, the team identified the optimal combination of Nkx2-1, Foxa1, Foxa2, and Gata6 to induce conversion most effectively. Experiments showed that approximately 4% of cells were successfully transformed into induced pulmonary-like epithelial cells (iPUL) exhibiting AT2 characteristics, including typical lamellar body structures and gene expression profiles highly similar to natural AT2 cells.
Professor Makoto Ishii of Nagoya University stated: "Direct reprogramming is not only faster but also carries lower tumor risk and offers the potential for autologous use." In animal experiments, transplanted iPUL successfully engrafted in the alveolar regions of diseased mice, with some further differentiating into alveolar type 1-like cells, demonstrating strong tissue repair capability.
This technology presents a potential therapeutic avenue for intractable respiratory diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The team's next step is to apply the technique to human cells and explore clinical translation. Professor Ishii noted: "Our ultimate goal is to develop safe regenerative therapies using patients' own cells."
This breakthrough not only simplifies the lung cell regeneration process but also provides new ideas for cell regeneration research in other organs. As the technology matures, it may enable personalized treatment for lung diseases in the future.