On 7 July, Spain's Centre for Energy, Environmental and Technological Research (CIEMAT), IBM, and its Spanish partner aggity announced a strategic partnership to integrate generative artificial intelligence (AI) into nuclear fusion experiments at CIEMAT's National Fusion Laboratory (LNF) in Madrid. The project, part of the European EUROFusion consortium, focuses on the TJ-II stellarator and plays a key role in Spain's participation in the ITER project.
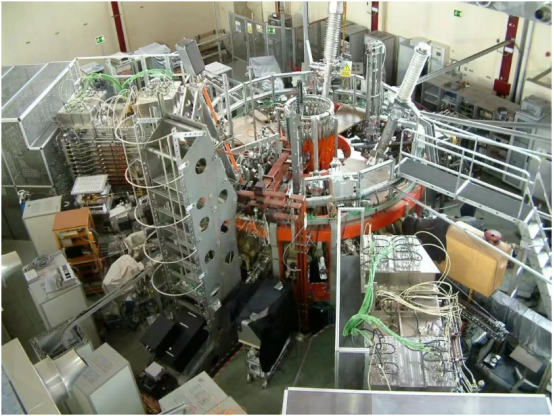
CIEMAT is a leading Spanish institution in advanced energy technology, heading national fusion research. Since 1998, its TJ-II helium-3 stellarator has been studying fusion physics principles and optimizing plasma parameters. Its complex magnetic field configuration enables high-precision exploration of plasma dynamics, contributing valuable data to ITER.
The integration of IBM's watsonx generative AI platform will transform how TJ-II experimental data is processed, enabling large-scale analysis and uncovering hidden patterns critical to advancing fusion research. Augusto Pereira, head of the LNF's AI project, said the team is connecting dedicated plasma parameter databases with predictive machine-learning applications and using generative large language models for pattern recognition. This will provide virtual assistants for short-term TJ-II operations, such as recommendation systems to improve confined plasma, search for effective experimental configurations, or generate daily run reports.
Manuel Villalba, IBM's Technology Leader for Spain, Portugal, Greece, and Israel, stated that IBM is committed to open innovation and that collaborating with CIEMAT to harness generative AI and the unique capabilities of watsonx deepens this commitment. Fusion is one of the most promising research directions for addressing energy challenges, and IBM is once again participating in a project to improve the world.
Watsonx, as IBM's portfolio for accelerating the impact of generative AI, is being used to implement use cases related to signal and image pattern recognition, experimental data classification, and predictive model generation. The project includes creating an AI platform dedicated to fusion data with a strong focus on security and adaptability.
Project progress includes: developing a hybrid-cloud model to enable flexible connection between the TJ-II system and IBM services for data processing; establishing a specialized vector database for efficient storage and retrieval of experimental data; training customized language models tailored to the unique data generated by the TJ-II device, with scientific validation of generative AI results.
The cooperation between IBM and LNF covers not only the technical level but also scientific research. Work has begun to precisely generate synthetic signals and images from fusion plasma observations, guiding generative AI to predictively and accurately "generate" synthetic nuclear fusion signals and images.
The collaboration between IBM Spain and CIEMAT's National Fusion Laboratory comes at a critical moment in fusion research. Nuclear fusion is considered one of the most promising solutions to future energy challenges, with international projects such as ITER in France, managed by the EU nuclear agency, leading the way. TJ-II plays a complementary role in the global research network by generating key data for theoretical models and computational simulations. By integrating generative AI technology, LNF-CIEMAT is at the forefront of scientific innovation, optimizing data analysis and accelerating exploration.
The National Fusion Laboratory is involved in the design and construction of several ITER diagnostic devices. Through its cooperation with IBM, it is positioning itself as a key player in future nuclear fusion efforts. Integrating advanced AI and autonomous systems into diagnostic monitoring represents a qualitative leap toward safer, more efficient, and more autonomous operation.
The project aims to specialize language models using specific fusion data to enable advanced semantic approaches for signal and image pattern recognition, improve data analysis capabilities, promote more precise scientific hypothesis generation, and accelerate the validation of theoretical models. The overall goal is to create a generative AI platform that fully leverages LLMs and ML capabilities trained specifically on fusion data to achieve advanced analysis and insight discovery.
CIEMAT is a public research institution focused on energy and environmental fields, with main activities including research and optimization of different energy sources and development of new technologies. LNF is the primary national reference institution in fusion energy research. In addition to operating TJ-II, it coordinates approximately 30 universities, other R&D centers, and industry participants in European projects and research within the EUROFusion and F4E frameworks. IBM is a global leader in hybrid cloud, artificial intelligence, and consulting expertise, helping clients leverage data insights, optimize business processes, and gain competitive advantage.