Among the various magnetic confinement fusion approaches, the stellarator confines plasma using a unique three-dimensional magnetic field. It offers advantages such as steady-state operation and immunity to disruptions, with fusion power scaling as the fourth power of the magnetic field strength. High-temperature superconducting (HTS) materials possess extremely high current-carrying capacity, providing significant advantages in increasing fusion power and reducing device size. However, the most widely scalable HTS material, rare-earth barium copper oxide (ReBCO), exhibits unique electromagnetic and mechanical properties that pose new challenges for the design of three-dimensional stellarator coils.
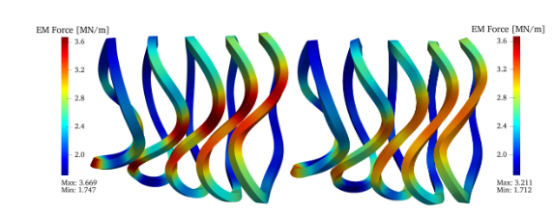
Recently, the Advanced Stellarator Team from the Department of Plasma Physics and Fusion Engineering has developed FOCUS-HTS, a new program for optimizing the design of three-dimensional HTS coils, building upon their independently developed FOCUS code [Nucl. Fusion 58 (2018) 016008; Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 60 (2018) 065008]. The coil centerline is parameterized using Fourier or B-spline methods, and a local centroid coordinate system with rotation angle parameters is constructed along the centerline to describe the finite cross-section of the 3D coil. The design objective uses the normal magnetic field error as the physical constraint, while key engineering parameters such as coil length, curvature, torsion, and spacing are treated as engineering constraints. The unique properties of HTS materials—including material strain, electromagnetic forces on the coil, and superconducting critical current density—are fully incorporated into the coil design to ensure that the 3D HTS coils simultaneously satisfy magnetic field distribution requirements, engineering feasibility, and the distinctive characteristics of HTS materials.
Using the Wendelstein 7-X stellarator coils and a precise quasi-axisymmetric (QA) stellarator as examples, this work demonstrates the capability of FOCUS-HTS to optimize existing coils for HTS performance and to perform integrated design of entirely new stellarators. The program is applicable to scenarios requiring three-dimensional HTS coils, such as stellarators and accelerators.