From smart grids to the Internet of Things, the modern world increasingly relies on interconnectivity between electronic devices. Thanks to researchers at the University of Ottawa, these devices can now be connected and powered over long distances using simple optical fiber — even in the harshest environments.
This represents a major advance in the development of photonic power converters (devices that convert laser light into electricity), opening the door to integrating laser-driven remote power solutions into existing fiber-optic infrastructure. In turn, this could pave the way for improved connectivity and more reliable communications in remote areas and extreme conditions.
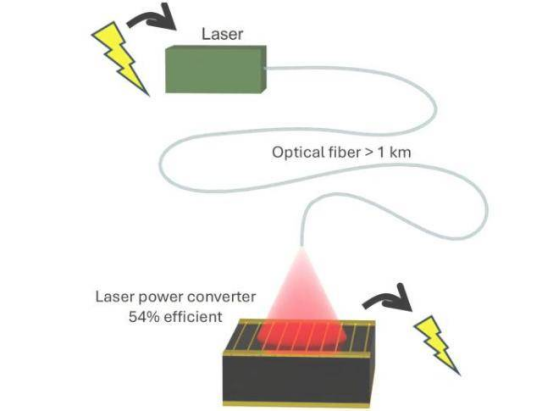
"In conventional fiber-optic power systems, most of the laser energy is lost," explains Professor Karin Hinzer of the University of Ottawa's SUNLAB, which conducted the research in collaboration with Germany's Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems. "With these new devices, the fiber can be much longer."
To address this challenge, the SUNLAB team developed a simulation model for a multi-junction photonic power converter operating at infrared telecommunications wavelengths, which exhibit very low attenuation loss per kilometer in optical fiber. "The fabricated devices demonstrated significant improvements in power and data transmission efficiency over distances exceeding one kilometer — distances at which conventional systems are simply not viable," added Gavin Forcade, first author of the paper published in Cell Reports Physical Science.
Integrated Power and Fiber-Optic Sensing
"Multi-junction" means these devices consist of many stacked semiconductor junctions that absorb light, allowing more of the laser to be converted into electricity and achieving higher efficiency and voltage. Using this model, the team designed and manufactured a photonic power converter that produces over 2 volts at its maximum power point with an efficiency exceeding 53%.
Photonic power converters operating at telecommunications wavelengths can enable more reliable telecom networks, reduce costs by enhancing system performance, and create faster, more robust networks, benefiting numerous technologies such as:
Smart grid monitoring
Lightning-protected wind turbine blade sensors
Spark-free fuel gauges on aircraft
Distributed IoT sensors
Remote camera links
Underwater sensors
Free-space laser power delivery for future applications such as simultaneous power and communication to drones, satellites, and lunar rovers
"This could power high-voltage and monitoring sensors in smart grids while avoiding the risk of lightning-induced failures, reduce spark risks in hazardous environments, and potentially deliver both power and data simultaneously to remote devices over existing fiber infrastructure," added Hinzer, University Research Chair in Photonic Devices for Energy.