The Helmholtz Munich Research Center in Germany, in collaboration with the Medical University of Vienna in Austria, has published an innovative achievement in Nature Biomedical Engineering. They developed a new endoscopic imaging technology named "O2E" that combines optical coherence tomography and photoacoustic imaging to detect microvascular and structural changes in esophageal tissue, significantly improving the accuracy of early cancer diagnosis.
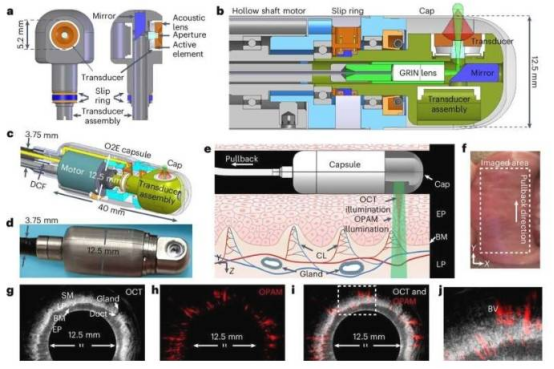
The research team integrated two imaging sensors into a capsule endoscope, enabling 360-degree full-field scanning. Project leader Professor Vasilis Ntziachristos stated: "Our dual-imaging system can detect early cancerous features that traditional methods cannot identify." In tests on tissue samples from Barrett's esophagus patients, the system successfully distinguished between healthy tissue, precancerous lesions, and malignant tumors.
The technology has received support from the European Innovation Council. Researcher Dr. Qian Li pointed out: "We are further optimizing the system and plan to integrate confocal endoscopy technology." This technology is expected to reduce the need for biopsies and lower medical costs. Currently, the treatment cost for late-stage esophageal cancer is approximately 14 times higher than that for early-stage treatment.