Crack identification plays a pivotal role in monitoring civil infrastructure. While traditional detection methods have achieved certain results, they heavily rely on manpower and offer limited efficiency. To address this challenge, a new study proposes a fully autonomous crack detection framework that leverages artificial intelligence and drone technology to enable autonomous crack segmentation and detection.
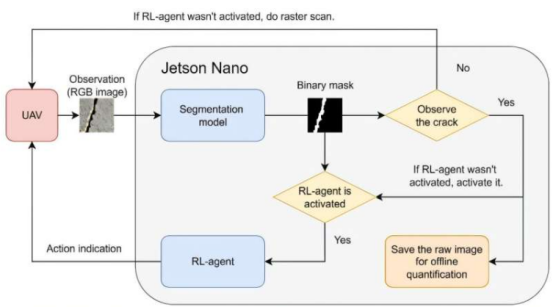
The autonomous crack detection framework relies on deep reinforcement learning to train an autonomous agent capable of adaptively tracking crack patterns. This agent can navigate independently without human intervention and intelligently adjust its search strategy based on crack features to maximize detection efficiency. Research data show that the system successfully captured over 85% of cracks in the training dataset and achieved 82% coverage in the test dataset. Moreover, compared to traditional exhaustive search methods, the new system improved computational resource efficiency by 64%, demonstrating significant potential for practical deployment on drones and other edge devices.
Corresponding author Professor Rih-Teng Wu stated: "The proposed framework demonstrates how the integration of artificial intelligence and drones can transform structural health monitoring into a safer, faster, and more reliable process." This innovative framework not only significantly reduces the time and labor costs required for structural health monitoring but also increases inspection frequency, enabling earlier detection of potential structural issues and thereby enhancing the safety and durability of civil infrastructure. As the technology continues to advance, the autonomous crack detection framework is expected to find widespread application in more fields, bringing revolutionary changes to the domain of structural health monitoring.