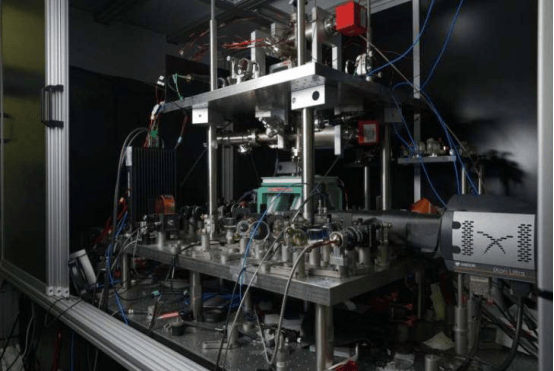
A research team from the James Watt School of Engineering at the University of Glasgow has successfully achieved real-time precise control of a robotic arm using open-source mobile network technology. Published in Communications Engineering, this study demonstrates the technology's application in simulated dental examinations, providing a new technical solution for future telemedicine.
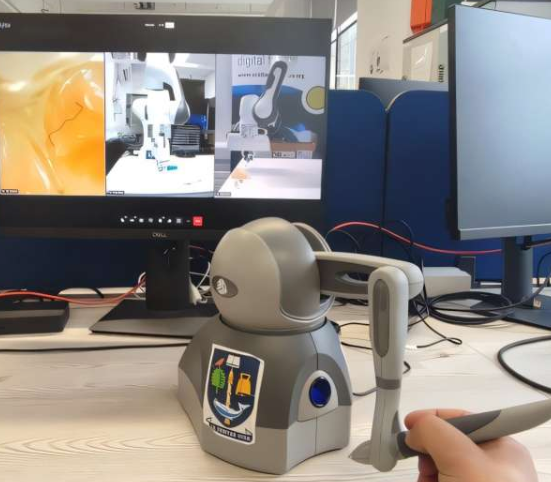

The research team employed the Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) framework to connect a haptic controller and robotic arm via a 4G LTE mobile network. The system uses commercial mobile network adapters to establish stable connections and optimizes signal quality and data transmission performance in real time through dedicated software. In a laboratory environment, this open-source mobile network technology achieved 10Mbps bandwidth communication between the base station and robotic arm, with latency controlled within 1 second, successfully completing simulated prosthetic dental examinations.
The system's energy consumption significantly outperforms traditional solutions. The mobile dongle used in the study consumes only 4.5 watts of power, reducing energy use by 90% compared to software-defined radio equipment required for the same tasks. This low-power characteristic provides an advantage for the long-term application of open-source mobile network technology in the medical field.
Professor Muhammad Imran, Dean of the James Watt School of Engineering, stated: "With the emergence of low-latency, high-reliability communication links, the skill internet is now one step closer to us. The Open RAN framework makes these technologies more affordable and accessible."
First author Dr. Saber Hassouna noted: "The test platform we developed using commercial hardware demonstrates that open-source mobile network technology can achieve outstanding performance in remote robotic operations. For applications like dental surgery, the robotic arm must move very smoothly, which requires high data throughput and low latency—both of which we achieved for the first time with this technology."
Professor Qammer Abbasi, Director of the Centre for Communication, Sensing and Imaging, said: "This is a highly encouraging demonstration, showing the technology's potential to achieve fine-grained, near-real-time control of robotic arms. We are currently further developing the system to ensure it maintains the same performance level over greater distances."
This research on open-source mobile network technology opens new possibilities for telemedicine. In the future, the technology is expected to enable doctors to provide medical services to patients in remote areas, while also holding application prospects in fields such as industrial automation and operations in special environments.