A new research achievement from the University of Nottingham has garnered attention in the high-end equipment manufacturing sector. Published in Robotics, the study focuses on methods to improve industrial robot positioning accuracy and lower operational costs.
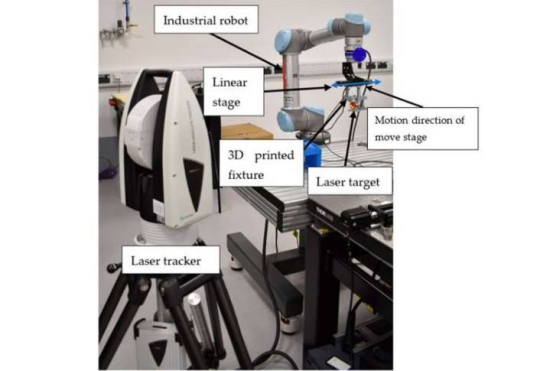
The internal motion resolution of industrial robots is limited by factors such as integrated sensors, control equipment precision, and installation software. Due to their heavy-duty design, specialized configurations, and the need for software modifications to enhance precision, these robots are difficult to replace easily. This minimizes downtime, contributing to lower production costs and maintenance expenses.
To improve robot motion resolution, the research team added an active gripper with higher motion resolution to the industrial robot, enhancing its capabilities beyond the original design. Additionally, a high-resolution joint was integrated into the robot, and laser tracking technology was used to provide precise 3D positional feedback for the system's end-effector—the part of the robot that interacts with the environment.
Experimental results showed that using a laser tracker significantly improved the positioning accuracy of the modified industrial robot, effectively meeting required operational standards. Analysis of 30 measurements for selected points indicated that the method increased positional accuracy by 82% compared to the original industrial robot controller.
Furthermore, the study demonstrated that laser tracker applications can effectively extend the lifespan of older robots, reduce production errors, and lower the costs associated with replacing inefficient legacy machines.
Dr. Mojtaba Ahmadieh Khanesar, researcher in the Advanced Manufacturing Technology Group, stated that the research findings are significant, enabling industrial robots to exceed expected motion resolution with minimal modifications. Inspired by this, the proposed method can be widely applied in areas such as pick-and-place operations, measurement applications, and additive manufacturing.