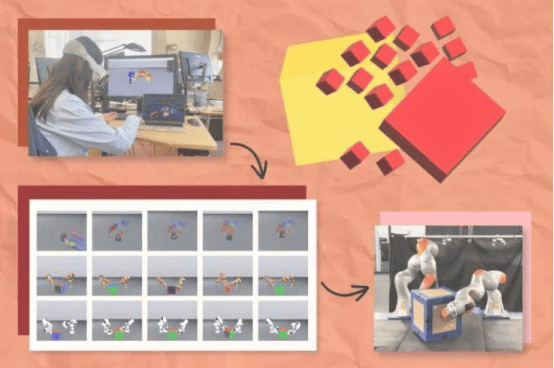
Diffusion models, a technology that has shone brightly in image generation and design, are steadily expanding their applications. Recently, they have made remarkable progress in the field of robot design. Generative AI (GenAI) models can now autonomously—or guided by user input—design robot structures and their control systems from scratch and simulate their performance before manufacturing. Researchers at MIT's Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) have taken this technology to the next level by developing a new approach that applies diffusion models to improve human-designed robots. Users can sketch a 3D model of a robot, specify which parts and dimensions to modify, and GenAI will brainstorm, optimize the design, and test it in simulation. Once a suitable design is found, the robot can be directly 3D-printed and operated without further adjustments.
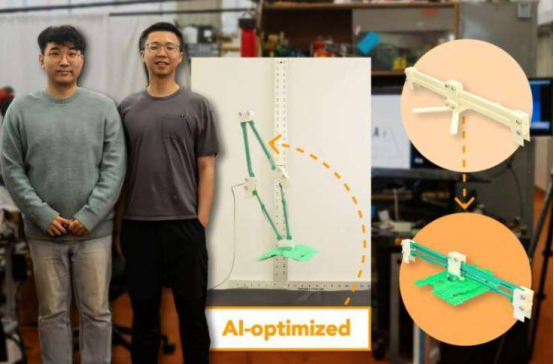
Robots built using this method achieved an average jump height of about 2 feet—41% higher than comparable robots. The key difference lies in the AI-generated curved linkages that resemble thick drumsticks, in contrast to the straight rectangular links used in standard robots. To further boost performance, the researchers sampled 500 potential designs, selected the top 12 based on simulated performance, refined the embedding vectors, and repeated the process five times. The final design resembled a sphere and dramatically improved jumping ability. Co-lead author and CSAIL postdoctoral researcher Byungchul Kim noted that the strength of diffusion models lies in their ability to discover unconventional solutions—such as storing energy through unique shapes—while avoiding overly thin links that could easily break.
The team also tasked the system with designing optimized feet to ensure safe landings. After repeated optimization, the AI-designed robots fell far fewer times than the baseline, achieving an 84% improvement. The success of diffusion models in enhancing both jumping and landing capabilities points to their broad potential in other areas of machine design. For example, manufacturing or household robot companies could use similar methods to improve prototypes and save engineers significant iteration time. Co-lead author and MIT CSAIL PhD student Tsun-Hsuan "Johnson" Wang said the project marks the beginning of using generative AI to create new kinds of robots, and he hopes to expand it to more flexible goals in the future—such as using natural language to guide the design of robots that can pick up a cup or operate a drill. Kim added that diffusion models hold promise for generating joints and devising novel ways to connect components, further elevating robot performance.