A research team from the University of Bonn in Germany has published findings in The Journal of Physiology, developing a gene therapy method targeting scar tissue after heart attacks. This method significantly reduces the risk of arrhythmias by enhancing electrical conductivity in fibroblasts within scar tissue.
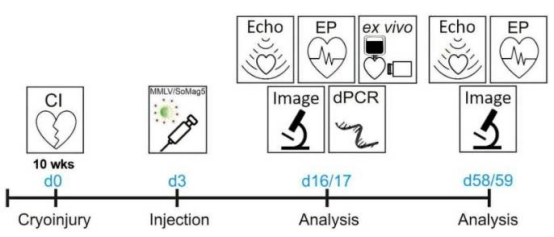
The research team used Moloney murine leukemia virus (MMLV) complexed with magnetic nanoparticles as a gene vector, guiding the connexin 43 gene into cardiac fibroblasts under a magnetic field. Professor Wilhelm Röll stated: "The innovation of this method lies in the viral vector's ability to specifically target fibroblasts rather than cardiomyocytes." Experimental data showed that treated mice had a 50% lower probability of arrhythmias compared to the control group.
The study addresses a key challenge in heart disease treatment. Professor Bernd K. Fleischmann noted: "The lack of electrical conductivity in scar tissue is the main cause of arrhythmias." By enhancing electrical connections between fibroblasts, this method holds promise for improving cardiac function recovery.
The research team also combined the fluorescent reporter gene mCherry, successfully validating gene delivery effectiveness in mouse models. Postdoctoral researcher Dr. Miriam Schiffer stated: "We achieved efficient transduction of scar tissue cells, which is of great significance for treating cardiac injury."
Although the method shows clinical application potential, the researchers indicate further validation is needed. Dr. Timo Mohr added: "The next step is to find suitable vectors for human cells and test in large animal models." This technology may also be applied to treatment areas beyond the cardiovascular system in the future.