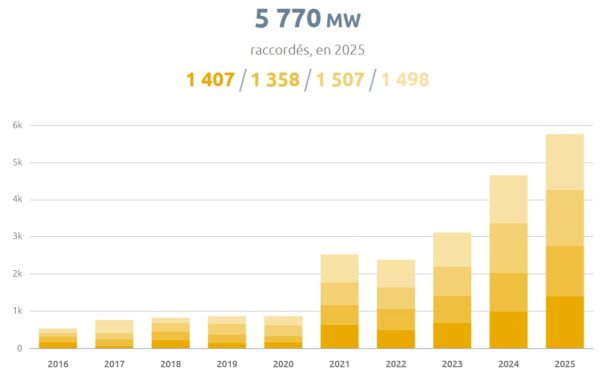
Wedoany.com Report-Apr. 20, The US-based safety certification organization UL has revised its testing methodology for assessing thermal runaway risks in battery energy storage systems (BESS). The updated standard, the fifth edition of ANSI/CAN/UL 9540A, aims to enhance safety evaluations for energy storage technologies.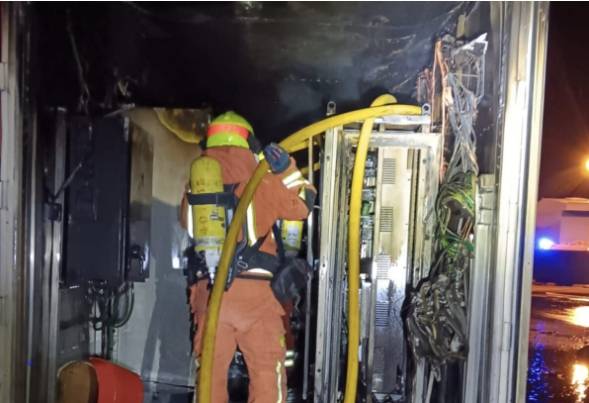
The revisions provide clearer guidelines for evaluating cell-to-cell propagation of thermal runaway, a chemical reaction that triggers rapid increases in temperature and pressure within battery cells, potentially leading to fires or explosions. These updates ensure more precise assessments to mitigate such risks.
UL developed the changes in collaboration with the energy storage industry, regulatory bodies, UL’s technical committee, and fire safety experts. The revised standard introduces high-temperature testing methods tailored to various battery chemistries, including sodium-ion batteries. It also incorporates new protocols for emerging BESS applications, such as installations on rooftops and in open garages, addressing the evolving needs of the sector.
These enhancements reflect UL’s commitment to advancing safety standards in response to technological advancements and industry feedback. The updated ANSI/CAN/UL 9540A standard is expected to support safer deployment of battery energy storage systems across diverse applications, contributing to the reliability and sustainability of energy storage solutions.