Quantum chip and quantum network technologies have achieved a significant breakthrough. The international academic journal Nature published a new study online in the early hours of February 12th: Chinese scientists have successfully constructed the world's first large-scale quantum key distribution network based on integrated photonic quantum chips. This quantum network supports parallel communication for 20 chip users, with a networking capability reaching 3,700 kilometers, achieving internationally leading levels in both the scale of chip users and networking capability.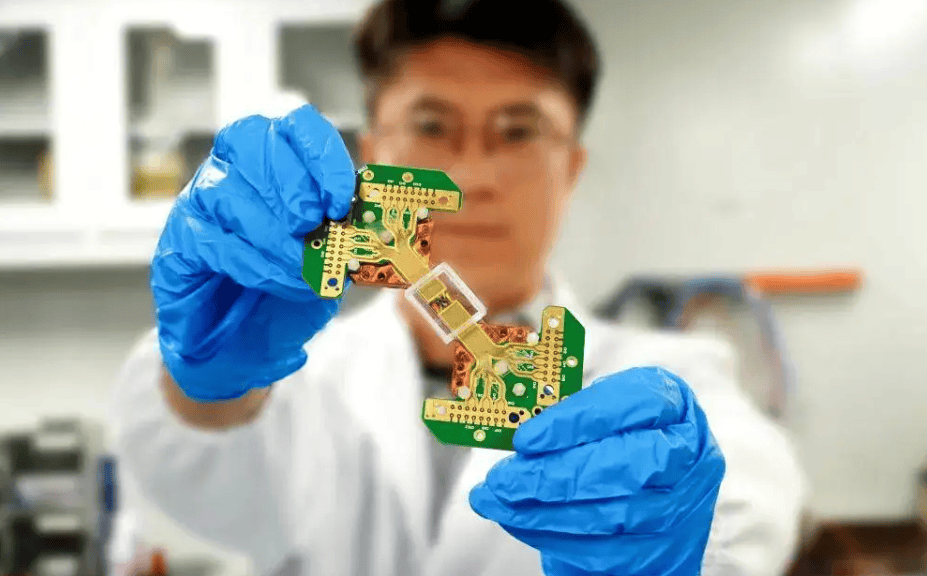
Quantum key distribution (QKD) transmits encryption keys via quantum states to achieve information encryption and ensure communication security. Twin-field quantum key distribution (TF-QKD), due to its advantages for long-distance quantum communication and supporting resource sharing at the detector end, has become an advanced QKD technology. However, because it imposes extremely high performance requirements on light sources and modulator devices, achieving the necessary hardware chip integration has been difficult to break through. Currently, this technology is mostly used for point-to-point QKD, and realizing multi-user, large-scale network systems faces challenges.
A research team led by Professor Wang Jianwei from the School of Physics at Peking University and Academician Gong Qihuang from the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a series of high-performance, fully functional integrated photonic quantum chips. Building on this, they successfully constructed a twin-field quantum key distribution network containing 20 quantum chip nodes.
Wang Jianwei said this is the first demonstration of a quantum key distribution network based on photonic quantum chips in over 20 years internationally. The experiment shows that the photonic quantum chips developed by the team possess high uniformity in wafer-level fabrication, promising low-cost mass production. This lays a technical foundation for building longer-distance, multi-user quantum key distribution networks.
"The quantum key distribution chip network is one of the important paths towards system miniaturization and device practicality," he stated. High-performance, low-cost photonic quantum chips hold great potential in promoting the large-scale application of quantum networks.
Reviewers for Nature believe this work represents significant progress in quantum chip and quantum network technology. The demonstrated quantum chip network possesses remarkable large-scale scalability and "will undoubtedly have an important impact on the field of quantum communication."
"This is an example of integrated photonic quantum technology advancing quantum communication development," said Gong Qihuang. He believes this achievement provides a feasible solution for constructing large-scale quantum communication chip networks and is of great significance for promoting the miniaturization, practicality, and scaling of quantum communication systems.