Wedoany.com Report-Sept. 10, China’s first offshore carbon dioxide storage demonstration project has reached a cumulative storage volume of more than 100 million cubic meters, according to China Central Television (CCTV). The project, located in the Pearl River Estuary basin in Guangdong Province, is operated by China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC). This milestone is regarded as an important step in advancing the country’s “dual carbon” goals and supporting the transition to green and low-carbon development.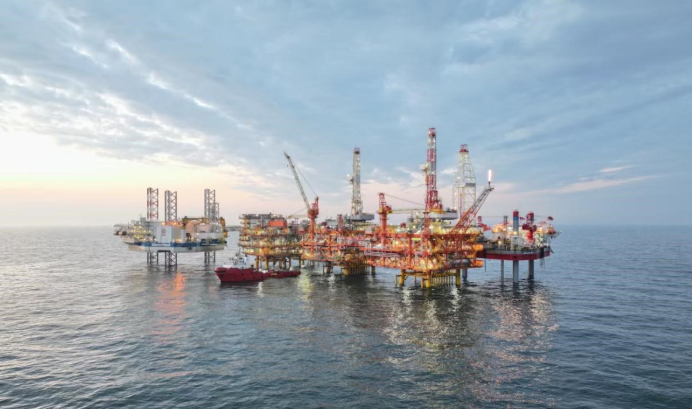
A CNOOC offshore oil platform in the Bohai Sea.
The project is situated at the Enping 15-1 Oilfield, the first oilfield in the Pearl River Estuary basin with high carbon dioxide content. Since June 2023, CNOOC has been operating China’s first offshore carbon capture and storage (CCS) facility. The process involves separating carbon dioxide from the oil and gas stream, followed by dehydration, drying, compression, and reinjection into shallow saline formations through injection wells under high pressure. The system has an annual storage capacity exceeding 40 million cubic meters.
According to the report, the achievement demonstrates that China’s offshore CCS technology, equipment, and engineering capabilities have reached a mature stage. This provides a foundation for scaling up future projects and contributes to enhancing the overall efficiency of offshore energy operations.
In May this year, a carbon dioxide utilization project was put into operation at the site. This development enables the use of captured carbon dioxide to increase crude oil output by 200,000 tons, creating a full-chain system for capture, storage, and utilization. CCTV noted that this represents a new model of marine energy recycling that “uses carbon to enhance oil recovery and uses oil to secure carbon.”
Looking ahead, the Enping 15-1 Oilfield is projected to reinject more than 550 million cubic meters of carbon dioxide over the next decade. This effort is expected to support an additional 200,000 tons of crude oil production. Such integration of storage and utilization aligns with broader efforts to balance energy development with carbon reduction.
CCTV highlighted that the success of the Pearl River Estuary project illustrates China’s growing capacity to develop and deploy advanced CCS technology at scale. It underscores the strategic role of offshore oilfields in pioneering solutions that both enhance energy security and contribute to environmental sustainability.
By combining innovative engineering, geological research, and integrated operations, the project provides valuable experience for future offshore CCS initiatives. Its progress strengthens China’s position in advancing large-scale carbon reduction technologies and supports the ongoing transition to a low-carbon economy.